
Affiliate Disclosure
Note: This banner contains an affiliate link. If you click and make a purchase, we may earn a commission at no extra cost to you. This helps us maintain and improve our content for users like you, supporting our travel site operations.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated. One of the most dangerous and insidious types of cyberattacks is the zero-day attack. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the developer or the public, making them especially challenging to detect and defend against. In this article, we will explore what zero-day attacks are, how they function, and how antivirus programs work to combat these threats.
1. What is a Zero-Day Attack?
A zero-day attack is a cyberattack that targets a software vulnerability that has not yet been discovered or patched by the software developer. The term “zero-day” refers to the fact that the developer has had zero days to fix the vulnerability before it is exploited. These attacks are highly dangerous because they can occur before any security measures or patches are available, leaving systems open to exploitation.
Zero-day vulnerabilities are typically discovered by cybercriminals, but they can also be found by researchers or security experts. Once discovered, these flaws are used to gain unauthorized access to a system, steal data, or cause damage. Because zero-day exploits are unknown to the developer, there is no specific defense or patch available at the time of the attack, making them particularly difficult to mitigate.
2. How Do Zero-Day Attacks Work?
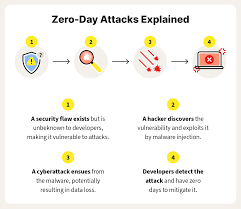
Zero-day attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software applications, operating systems, or network protocols that have not yet been identified by the vendor or the security community. When a cybercriminal discovers such a vulnerability, they can create malware or an exploit code specifically designed to take advantage of the flaw.
The attack typically works by tricking the software or system into executing malicious code that can compromise the system’s security. For example, an attacker may use a zero-day exploit to install malware, steal sensitive data, or gain control over the system without the user’s knowledge. These attacks can be delivered through various vectors, such as email attachments, infected websites, or compromised software downloads.
Once the attack is initiated, the malicious code can operate undetected, often bypassing traditional security defenses like antivirus software, which rely on known virus signatures or patterns to detect threats. This makes zero-day attacks particularly difficult to defend against and requires proactive and real-time security measures.
3. The Impact of Zero-Day Attacks

The consequences of a successful zero-day attack can be devastating. For individuals, these attacks may result in the theft of personal information, financial loss, or privacy violations. For businesses, the impact can be far-reaching, leading to data breaches, intellectual property theft, reputation damage, and legal consequences.
Zero-day attacks can also be used as part of larger cyber-espionage campaigns, targeting government agencies, corporations, or other organizations with valuable data. In some cases, zero-day vulnerabilities are sold on the dark web to other cybercriminals or nation-state actors who seek to exploit them for their own gain. The high stakes involved in these attacks make them a significant concern for cybersecurity professionals and organizations worldwide.
4. Why Zero-Day Attacks are Difficult to Detect

Zero-day attacks are notoriously difficult to detect because they exploit unknown vulnerabilities that antivirus programs and other security measures have not been updated to recognize. Traditional antivirus software relies on known virus signatures and patterns to identify threats, but since zero-day vulnerabilities are unknown, there is no signature for the antivirus software to match against.
Additionally, zero-day attacks often use highly sophisticated methods to bypass detection. They may employ techniques such as polymorphism (changing the code to avoid detection), rootkits (hiding malicious files deep within the system), or fileless malware (executing attacks directly in the system’s memory without leaving traces on disk). These methods make it incredibly challenging for security software to detect and block the attack in real time.
To make matters worse, zero-day exploits may remain dormant for an extended period, only activating when certain conditions are met. This delay makes it harder for antivirus programs to identify the threat before it causes significant damage.
5. How Antivirus Programs Combat Zero-Day Attacks

While traditional antivirus software may struggle to detect zero-day attacks, modern antivirus solutions have evolved to incorporate advanced techniques to combat these threats. Several strategies are used to identify and mitigate zero-day attacks, including behavior-based detection, machine learning, and cloud-based threat intelligence.
Behavior-Based Detection: Instead of relying on virus signatures, behavior-based detection looks for suspicious activity in the system that may indicate an attack. For example, if an application tries to modify system files or access sensitive data in an unusual way, the antivirus program may flag this as potentially malicious. By monitoring the behavior of programs in real time, antivirus software can identify zero-day threats based on the actions they take rather than the specific code they use.
Machine Learning and AI: Many antivirus programs now incorporate machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance their ability to detect zero-day attacks. These technologies analyze large volumes of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate the presence of a zero-day exploit. Over time, AI-powered antivirus solutions can learn from new data and adapt to evolving threats, improving their ability to detect previously unknown attacks.
Cloud-Based Threat Intelligence: Cloud-based threat intelligence allows antivirus software to access real-time data on emerging threats from around the world. This collaborative approach enables antivirus programs to detect zero-day attacks more quickly by sharing information about new vulnerabilities and exploits. Cloud-based systems can provide continuous updates to the antivirus software, ensuring that users are protected against the latest threats.
Sandboxing: Some antivirus programs use sandboxing techniques to isolate suspicious files and analyze their behavior in a controlled environment. This allows the antivirus program to observe how the file interacts with the system without risking damage to the user’s device. If the file exhibits malicious behavior, it is flagged and removed before it can cause harm.
6. Preventing Zero-Day Attacks with a Multi-Layered Approach
While antivirus software plays a crucial role in defending against zero-day attacks, it is only one part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. To effectively protect against these attacks, users and organizations should adopt a multi-layered approach to security.
Regular Software Updates: One of the most effective ways to defend against zero-day attacks is by keeping software up to date. Software developers regularly release patches and updates to fix known vulnerabilities, and applying these updates as soon as they are available can prevent zero-day exploits from taking advantage of unpatched flaws.
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Firewalls and IDS systems provide an additional layer of protection by monitoring network traffic and blocking malicious activities. These tools can detect unusual patterns of behavior, such as attempts to exploit vulnerabilities, and prevent attackers from gaining access to the system.
User Awareness and Training: Educating users about cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails and avoiding suspicious downloads, can help reduce the risk of falling victim to a zero-day attack. Users should also be encouraged to use strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible.
7. The Future of Zero-Day Attack Prevention
As cybercriminals continue to develop more sophisticated zero-day exploits, the fight against these attacks will require constant innovation. Advances in machine learning, AI, and behavioral analysis will continue to play a significant role in improving antivirus detection capabilities.
In the future, we may also see more collaboration between software vendors, cybersecurity firms, and government agencies to share information about new vulnerabilities and zero-day attacks. By working together, these entities can improve the overall security landscape and reduce the risk of zero-day exploits being successfully launched.
Conclusion
Zero-day attacks represent one of the most dangerous and elusive threats in the world of cybersecurity. These attacks exploit vulnerabilities that are unknown to developers, leaving systems defenseless until patches are issued. Antivirus programs, however, have evolved to combat these threats using advanced techniques such as behavior-based detection, machine learning, and cloud-based intelligence. To fully protect against zero-day attacks, it is essential to adopt a multi-layered security approach that includes regular software updates, firewalls, and user awareness. As technology continues to advance, so too will the methods for defending against these sophisticated cyber threats.

